What is the difference between the application of Amorphous Nanocrystalline Products' amorphous and nanocrystalline soft magnetic cores?
Magnetic cores Made of ferromagnetic metals or ferrimagnetic compounds, magnetic cores have high magnetic permeability and are widely used in electrical, electromechanical, and magnetic equipment to confine and guide magnetic fields. A magnetic field is generated by a current-carrying coil surrounding a magnetic core.
Using a magnetic core can increase the magnetic field strength in electromagnetic coil hundreds of times compared to not using a magnetic core.
However, considering the core loss, the magnetic core usually adopts "soft" magnetic materials with low coercive force and hysteresis such as amorphous core and nanocrystalline magnetism.
Frequency-dependent energy losses are caused by side effects such as eddy currents and hysteresis, and different operating frequencies require different core materials.
glassy metal
Amorphous metals are alloys of various amorphous or glassy states (eg Metglas). Materials are highly responsive to magnetic fields to reduce hysteresis losses, and they can also have low electrical conductivity to reduce eddy current losses. In addition, high mechanical strength and corrosion resistance are also beneficial for this application. Amorphous metals are ideal for making high-efficiency transformers.
Nanocrystalline
The nanocrystalline alloy is a standard iron-boron-silicon alloy with small additions of copper and niobium. The powder particle size can reach 10~100 nanometers. Nanocrystalline materials have excellent performance at lower frequencies, for example in choke coils for inverters and in high-power applications.
What Is The Difference Between The Application Of Amorphous Nanocrystalline Products's Amorphous And Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Cores?
Recommended Products
-
 View More >>
View More >>
Non-Toroidal C-Type Cut Amorphous Nanocrystalline Cores
Industry: Amorphous Nanocrystalline Core
-
 View More >>
View More >>
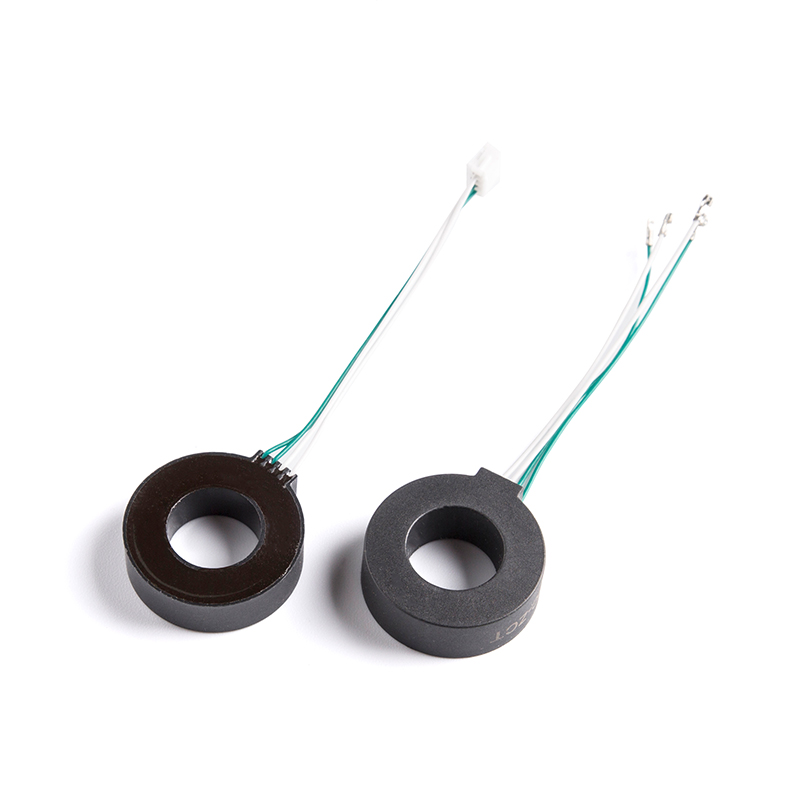
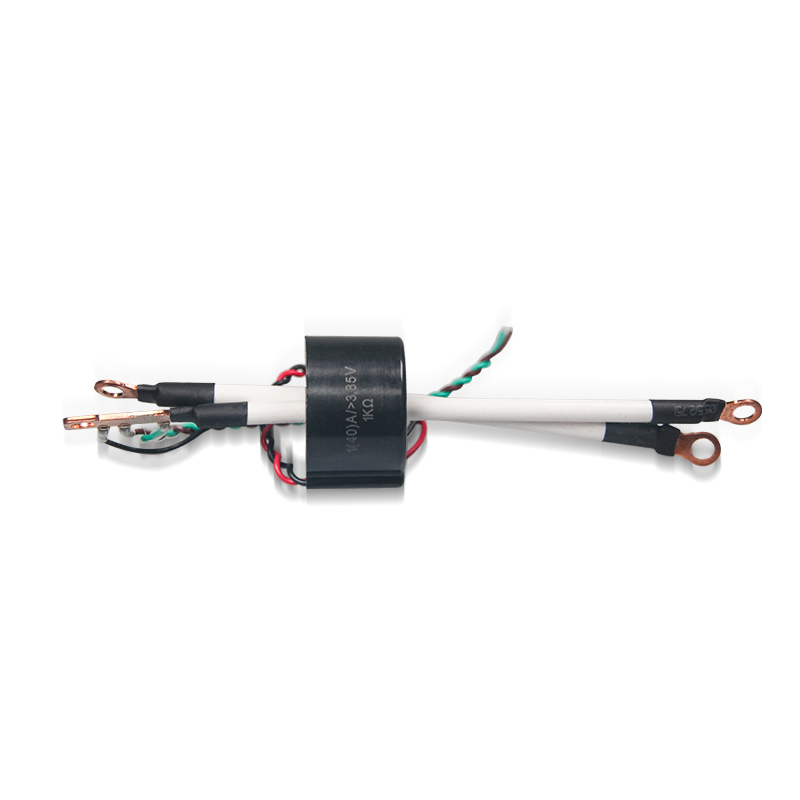
EHC-VCT Series for Power supply
Industry: Current Transformer
-
 View More >>
View More >>
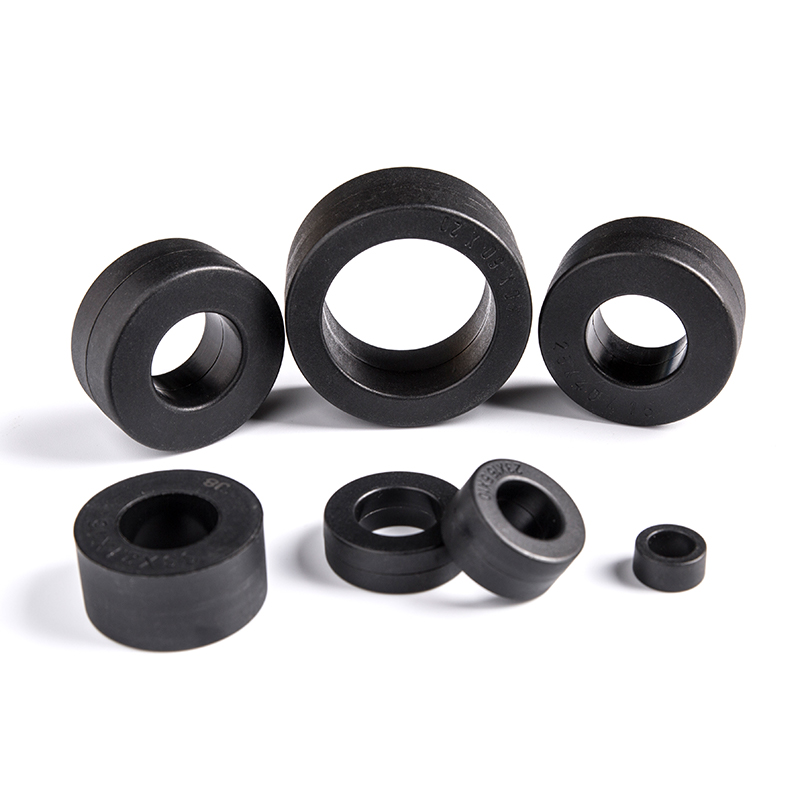
Transformers Cores Amorphous Nanocrystalline Cores
Industry: Amorphous Nanocrystalline Core
-
 View More >>
View More >>
Amorphous Nanocrystalline Inductor Cores
Industry: Amorphous Nanocrystalline Core
-
 View More >>
View More >>
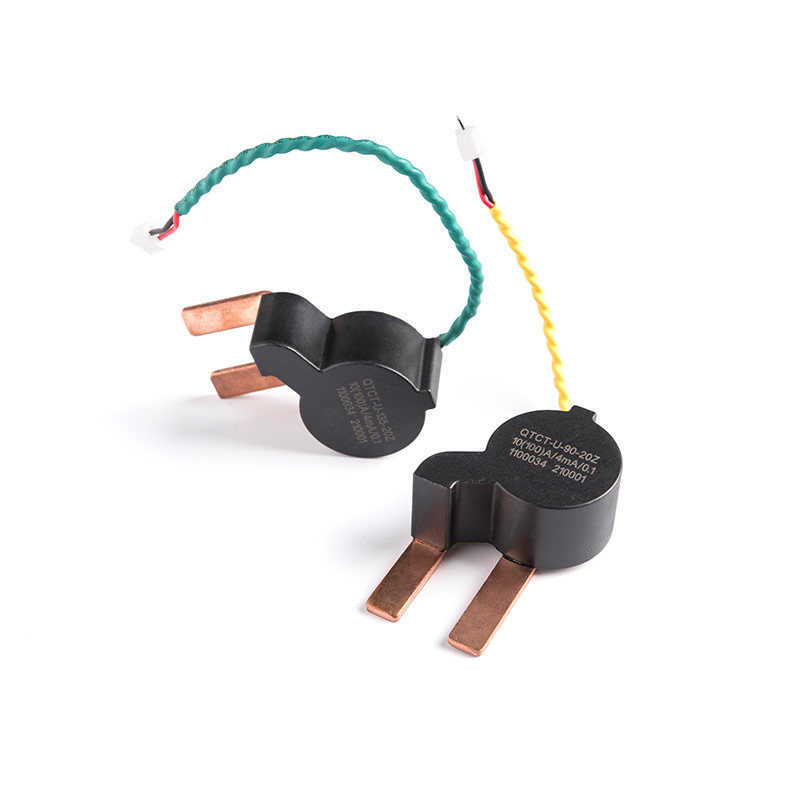
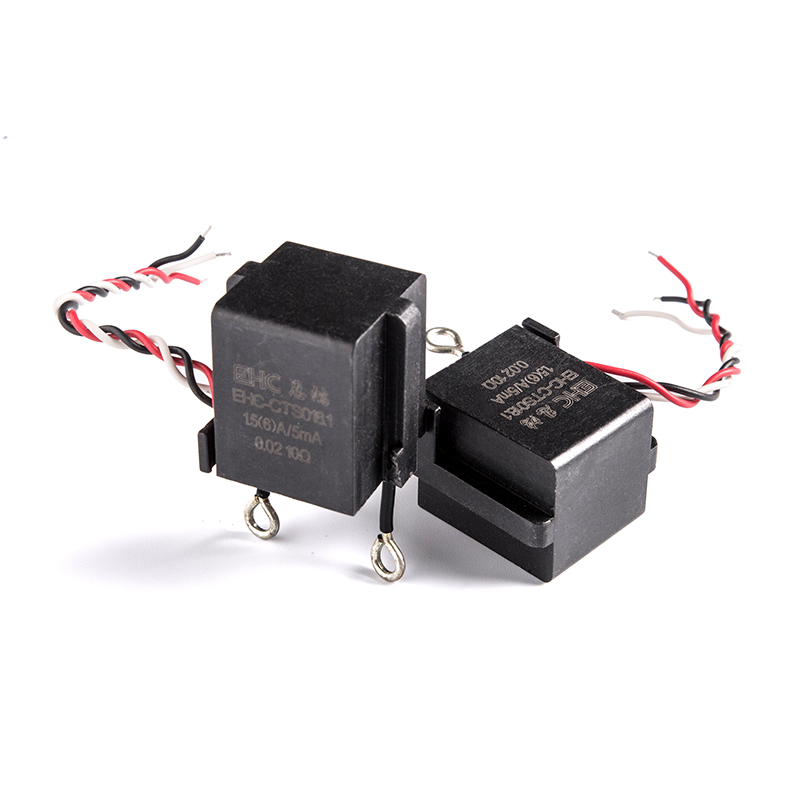
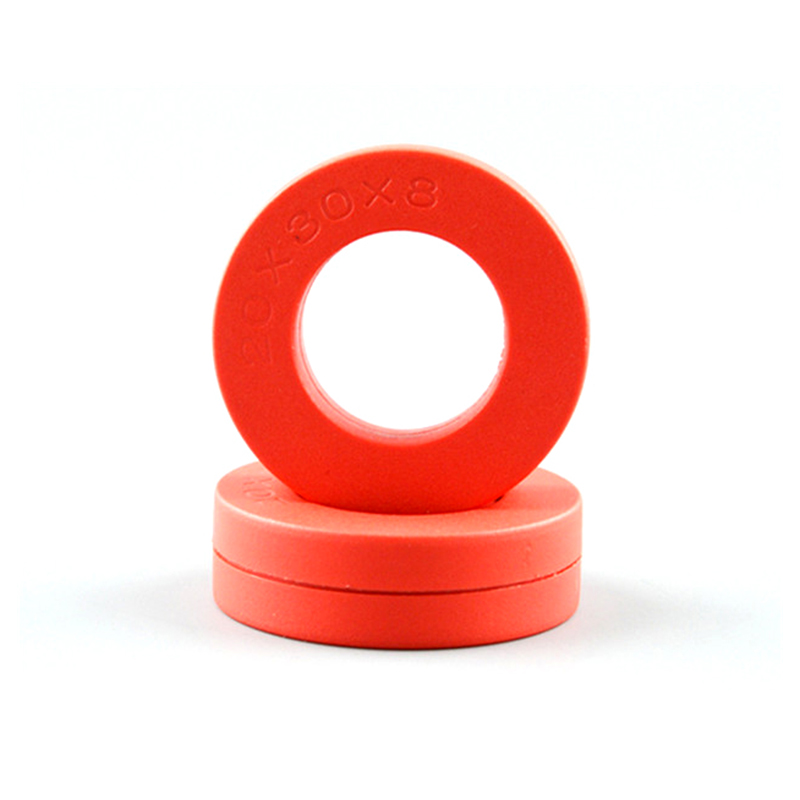
CTS Series Terminal High Precision Amorphous Nanocrystalline Current Transformers
Industry: Current Transformer
-
 View More >>
View More >>
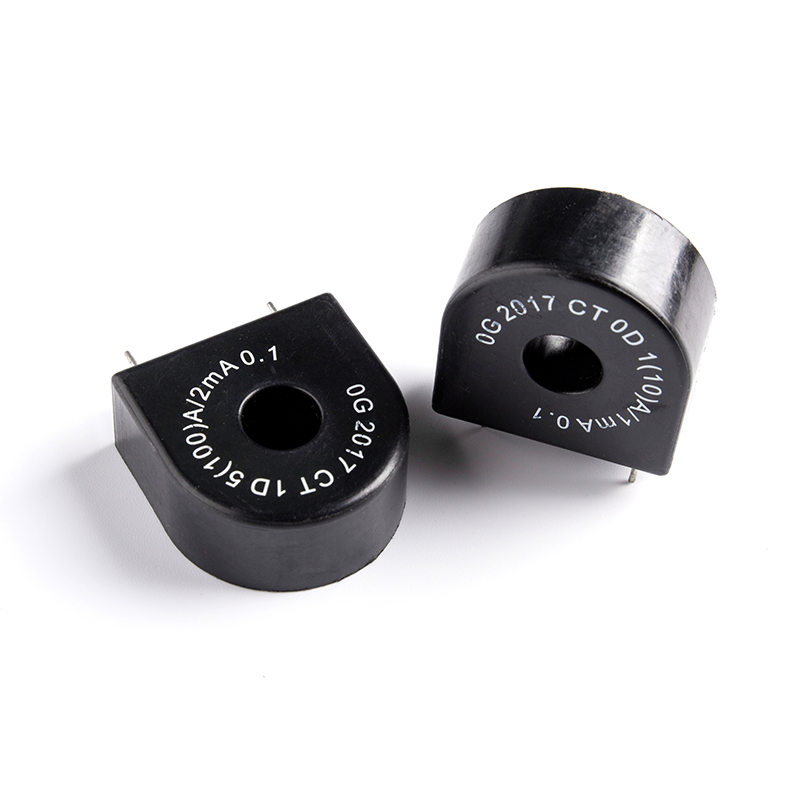
Rectangular hysteresis loop Cores
Industry: Amorphous Nanocrystalline Core
-
 View More >>
View More >>
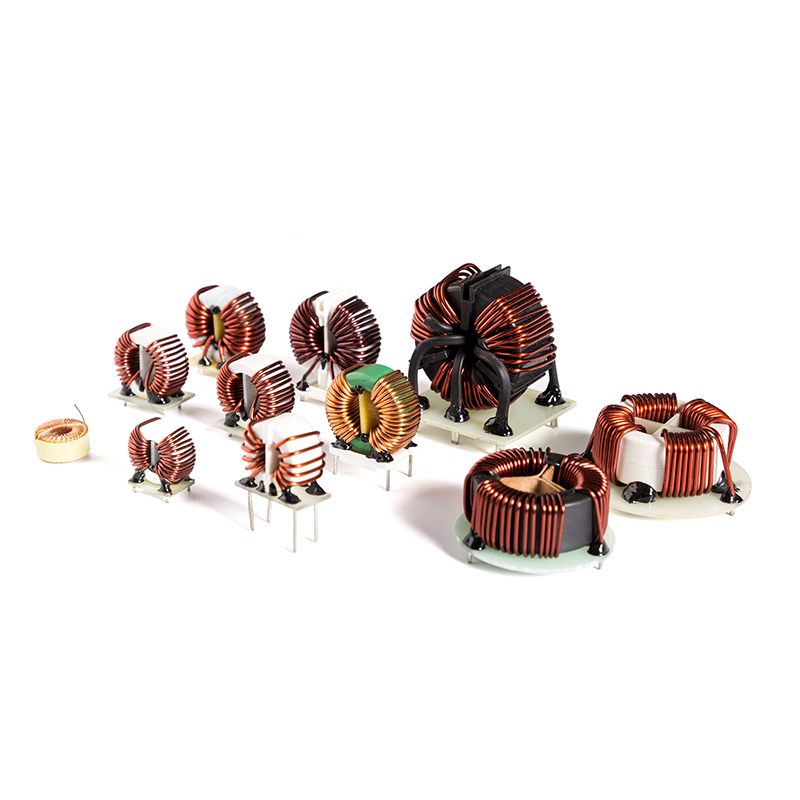
High Linear Current Transformers
Industry: Current Transformer
-
 View More >>
View More >>
Common Mode Choke Amorphous Nanocrystalline Inductors
Industry: Amorphous Nanocrystalline Inductors

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語

