In today's world of high-speed electronics and sensitive circuitry, electromagnetic interference (EMI) poses a significant challenge. One of the most effective tools in mitigating this interference is the common mode choke core — a passive component widely used across power supplies, communication systems, and industrial equipment.
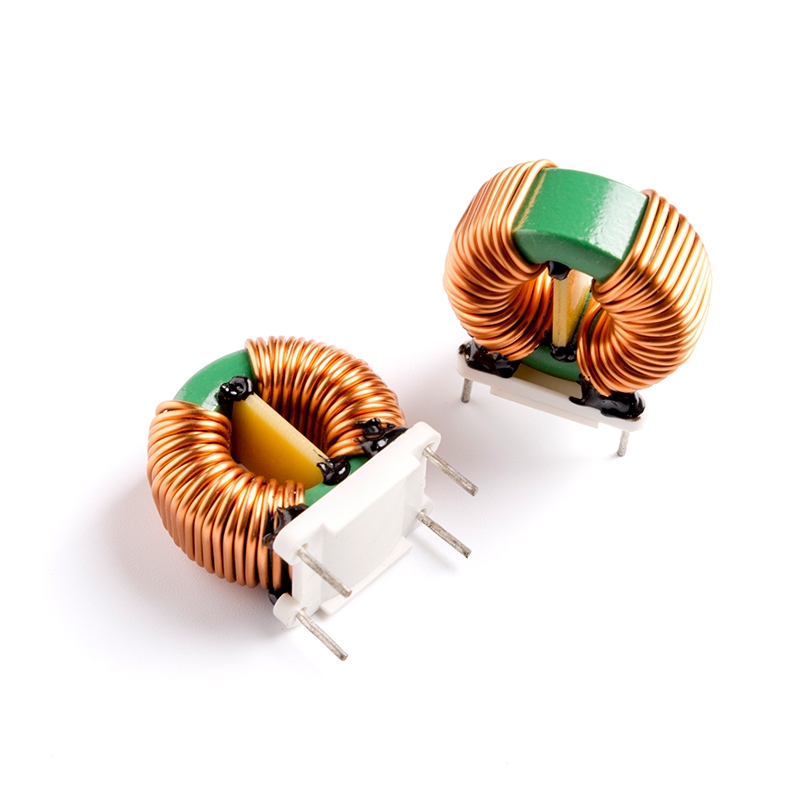
A common mode choke core , often simply referred to as a choke core , is a magnetic component designed to suppress common-mode noise in electrical circuits. It typically consists of two or more windings wrapped around a magnetic core made from materials like ferrite or powdered iron. These windings are wound in such a way that they cancel out differential signals while resisting the flow of common-mode currents.
The term common mode choke refers to its function: it "chokes" or blocks unwanted high-frequency noise that appears simultaneously on two or more conductors relative to ground.
How Does a Common Mode Choke Core Work?
When alternating current flows through the windings of a choke core, it generates a magnetic field. In normal operation (differential mode), the current flows in opposite directions in each winding, causing their magnetic fields to cancel each other out. As a result, the choke offers minimal impedance to the desired signal or power current.
However, during a common mode event , where noise appears equally on both lines with respect to ground, the magnetic fields reinforce each other. This creates a large impedance that attenuates the noise without affecting the main signal or power transmission.
This dual-winding configuration allows the common mode choke to effectively filter out EMI and radio frequency interference (RFI), making it indispensable in modern electronic design.
Materials Used in Common Mode Choke Cores
The performance of a choke core heavily depends on the magnetic material used. Some of the most commonly used materials include:
Ferrite cores : Known for high permeability and low losses at high frequencies, these are ideal for applications involving EMI suppression in switching power supplies.
Powdered iron cores : These offer good saturation characteristics and are often used in lower frequency applications.
Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials : These advanced materials provide superior performance in high-frequency and high-current environments.
Each type of core has unique properties that make it suitable for specific use cases, from consumer electronics to aerospace systems.
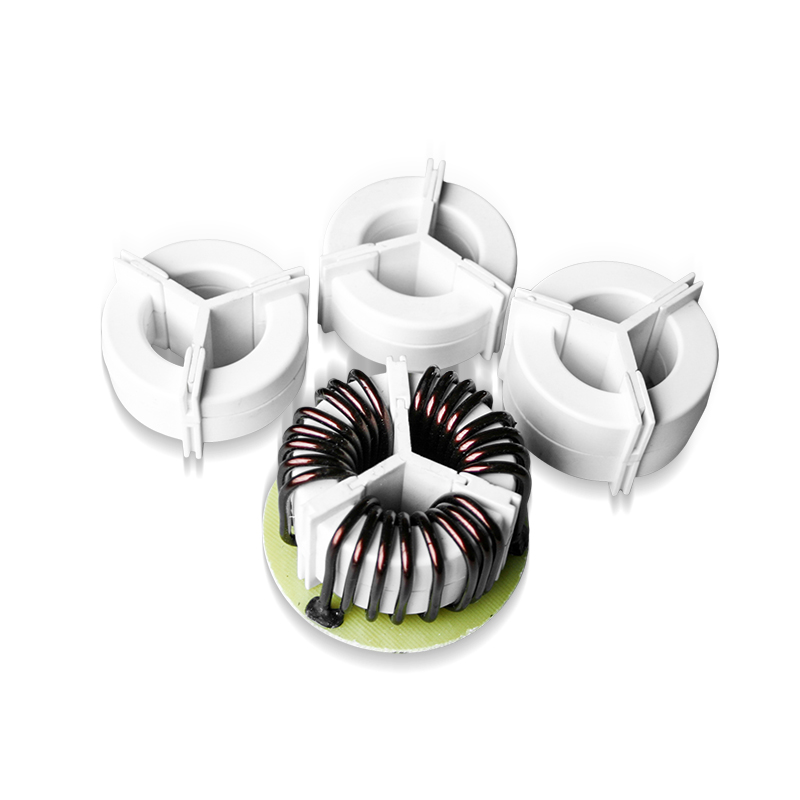

Key Applications of Common Mode Choke Cores
Common mode chokes are employed in a wide range of applications due to their effectiveness in filtering out unwanted noise. Some of the primary areas include:
Power supplies : In AC/DC and DC/DC converters, choke cores help reduce conducted emissions, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Communication interfaces : Ethernet, USB, and HDMI interfaces often incorporate choke cores to prevent data corruption caused by EMI.
Industrial automation : In factory settings, choke cores protect sensitive control systems from electrical noise generated by motors and relays.
Automotive electronics : Modern vehicles rely on choke cores to ensure reliable operation of onboard electronics amid high levels of electromagnetic activity.
These components play a critical role in maintaining signal integrity and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in complex electronic systems.
Design Considerations
When selecting or designing a common mode choke core , several factors must be considered:
Inductance value : Higher inductance provides better noise suppression but may also increase cost and size.
Current rating : The core must handle the required operating current without saturating.
Frequency range : Different applications require suppression over different frequency bands.
Impedance characteristics : Impedance should match the system requirements to ensure optimal noise rejection.
Engineers must carefully evaluate these parameters to choose the right choke core for their application.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語
 View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >>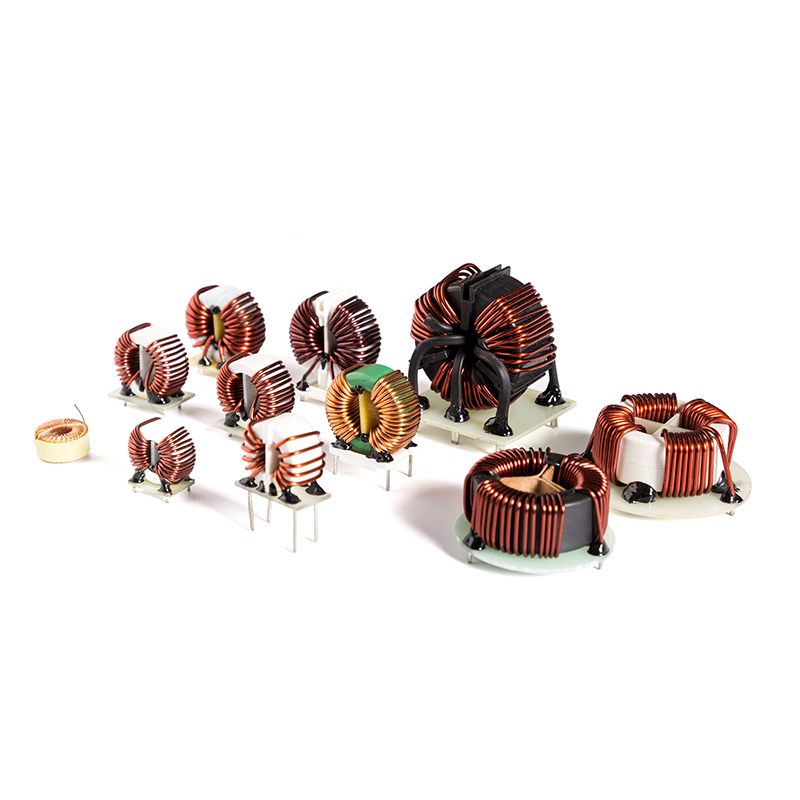 View More >>
View More >>