A current transformer (CT) and a voltage transformer (VT) serve different purposes in electrical systems.
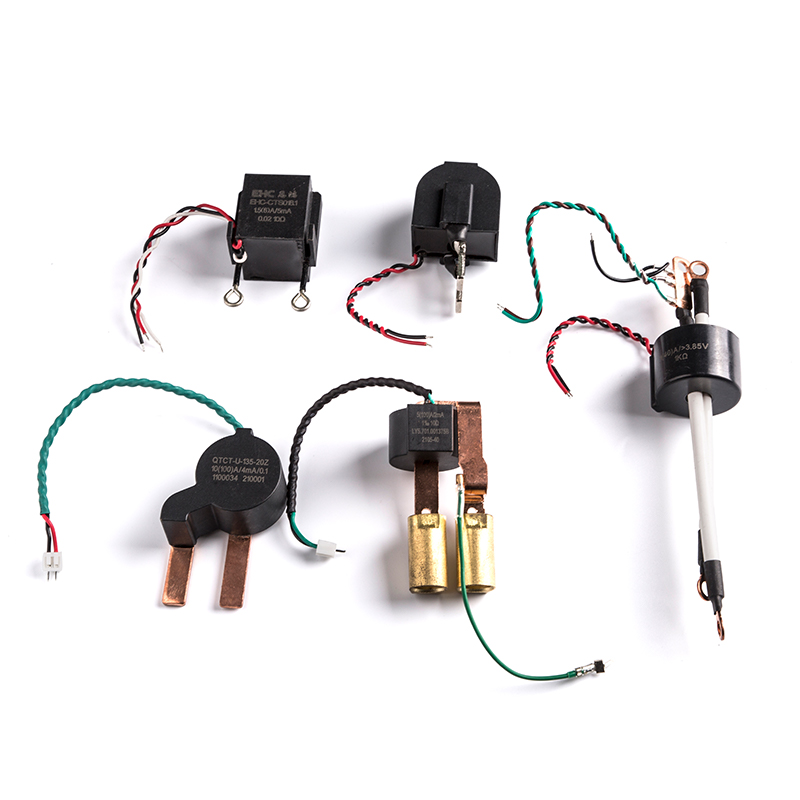
A current transformer is designed to measure alternating electric currents. It consists of a primary winding, through which the current to be measured passes, and a secondary winding, which is connected to the measuring or protective devices. The primary current is transformed to a lower, standardized value, typically suitable for measurement or protection purposes. CTs are commonly used in metering, protective relaying, and control systems to monitor and protect electrical circuits and equipment.
On the other hand, a voltage transformer, also known as a potential transformer, is used to measure voltage levels in electrical systems. It steps down high voltage to a lower, standardized value suitable for measurement or protection. Voltage transformers are commonly used in metering, protective relaying, and control systems to monitor and protect electrical circuits and equipment, similar to CTs.
Specific applications of CTs include:
Metering: CTs are widely used for measuring current in power systems, allowing for accurate monitoring of power consumption and load analysis.
Protective Relaying: CTs play a crucial role in protective relay systems by providing current inputs to protective devices, such as overcurrent relays, to detect and isolate faults in electrical systems.
Control Systems: CTs are used in control circuits to provide current signals for various control and monitoring functions in industrial and commercial applications.
Energy Management: CTs are employed in energy management systems to monitor and optimize power usage, identify inefficiencies, and improve overall energy efficiency.
Power Quality Analysis: CTs are utilized in power quality monitoring systems to measure and analyze current waveforms, harmonics, and other parameters to ensure the quality and reliability of electrical power.
In summary, while both CTs and VTs are essential components in electrical systems, CTs are specifically designed to measure current, and they find applications in metering, protective relaying, control systems, energy management, and power quality analysis.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語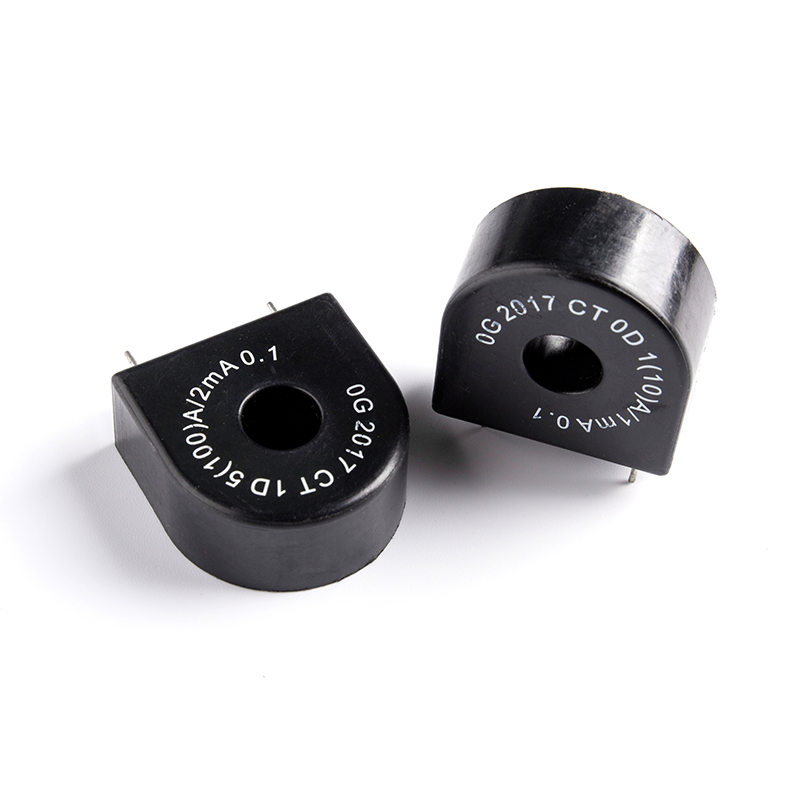
 View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >>