Current Transformer (CT) is a widely used device in power systems. It is mainly used to measure and monitor the size of current, and convert the large current in the high-voltage line into a relatively small current value, which is convenient for safe measurement and protection of equipment operation. The main function of the current transformer is to ensure the stability and safety of the system, especially in high-voltage power systems.
Working Principle
The working principle of the current transformer is based on the law of electromagnetic induction. When the AC current passes through the primary conductor, a magnetic flux is generated on the core of the current transformer, which induces current in the secondary winding. The current of the secondary winding is proportional to the current of the primary side, and is usually designed according to the current transmission ratio (such as 1000A/5A) to achieve the purpose of "reducing" the primary current. The reduced current can be safely transmitted to measuring instruments, relay protection devices and other equipment.
Current transformers are divided into metering type and protection type. Metering type current transformers are mainly used to measure the current size of equipment to ensure the metering accuracy of the power system. Protective current transformers are used to monitor abnormal currents in the system, such as overload or short circuit. When a system fault occurs, it will provide a signal to the protection device, which will trigger the protection mechanism and cut off the circuit to prevent equipment damage or casualties.

Application areas
Current transformers are widely used in all aspects of the power system, including power generation, transmission, distribution and monitoring of power consumption equipment. In power plants, substations and industrial facilities, they help monitor current changes in real time to ensure the stable operation of the system. Common applications include:
Current measurement: Current transformers reduce the large current in high-voltage lines and provide them to measuring instruments to achieve accurate monitoring of current.
Energy metering: It ensures that the reading of the energy meter is accurate, calculates the total energy consumption by measuring the current, and is widely used in the metering system of the power grid.
Relay protection: Current transformers can sense fault currents in the power system and transmit signals to the protection device in time to ensure the safety of the system.
Insulation monitoring: In some high-voltage cable systems, current transformers can also help monitor the insulation status of the cable to prevent potential faults.
With the increasing complexity of power systems, current transformers will become more intelligent in the future. The development trend of smart grid requires high-precision, wide-range current transformers to meet higher system requirements. At the same time, the application of new materials also makes it possible to optimize the size, performance and cost of current transformers. The future development direction of current transformers also includes better anti-interference performance, a wider current range, and higher integration with intelligent monitoring systems.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語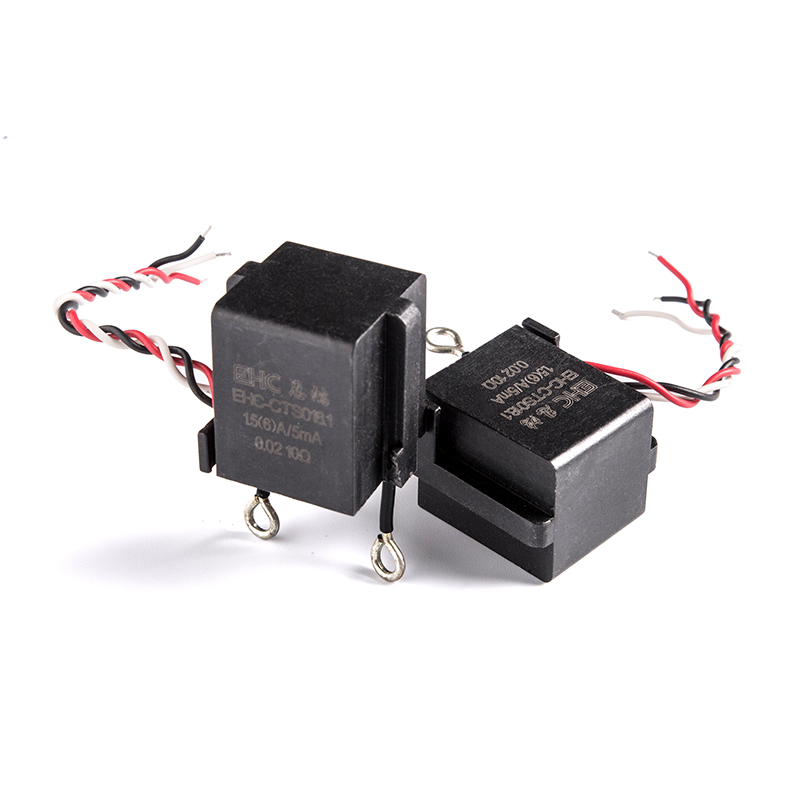
 View More >>
View More >>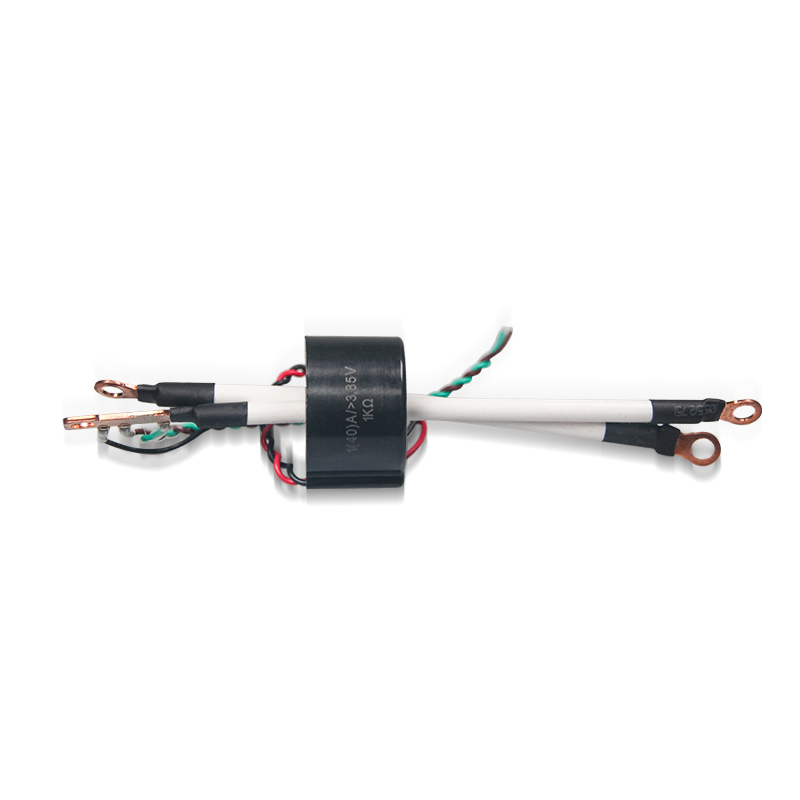 View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >> View More >>
View More >>